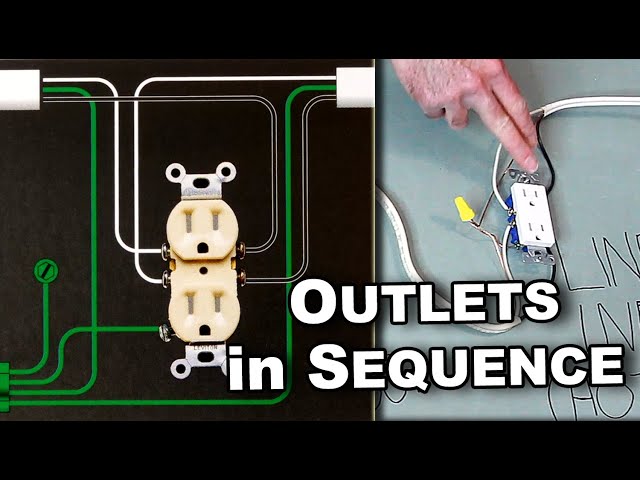
Wiring electrical outlets in series involves connecting the outlets sequentially, with the output of one outlet serving as the input for the next. This method of wiring differs from parallel wiring, where each outlet receives power directly from the electrical panel. A series diagram illustrates the sequence of connections, showing the flow of electricity from the power source through each outlet.
Wiring outlets in series offers several advantages. It is a relatively simple and cost-effective method, requiring less wire and fewer connections compared to parallel wiring. Additionally, series wiring can provide greater flexibility in controlling multiple outlets from a single switch. By incorporating switches in the series circuit, homeowners can conveniently turn on or off multiple outlets simultaneously, which can be useful for controlling lighting or other electrical appliances.
However, it is important to note that series wiring also has some limitations. The current flowing through each outlet is the same, which means that adding additional outlets to the circuit will decrease the voltage available to each outlet. This can potentially lead to voltage drop issues, especially if high-power devices are connected to the circuit. Furthermore, if one outlet in the series fails, it can disrupt the entire circuit, affecting the power supply to all subsequent outlets.
Wiring Electrical Outlets in Series Diagram
Wiring electrical outlets in series involves connecting outlets sequentially, with the output of one outlet serving as the input for the next. This method of wiring differs from parallel wiring, where each outlet receives power directly from the electrical panel. A series diagram illustrates the sequence of connections, showing the flow of electricity from the power source through each outlet. Here are six key aspects to consider when wiring electrical outlets in series:
- Simplicity: Series wiring is relatively simple and straightforward to implement.
- Cost-effectiveness: It requires less wire and fewer connections compared to parallel wiring.
- Flexibility: Series wiring allows for greater flexibility in controlling multiple outlets from a single switch.
- Voltage Drop: Adding additional outlets to the circuit can decrease the voltage available to each outlet.
- Circuit Disruption: If one outlet in the series fails, it can disrupt the entire circuit.
- Power Limitations: Series wiring may not be suitable for circuits with high-power devices.
These aspects highlight the advantages and limitations of wiring electrical outlets in series. By carefully considering these factors, electricians and homeowners can determine the most appropriate wiring method for their specific needs. It is important to consult with a qualified electrician for professional advice and to ensure that all electrical work is carried out safely and in accordance with local codes and regulations.
Simplicity
The simplicity of series wiring stems from its fundamental design. Unlike parallel wiring, which requires multiple connections from the power source to each outlet, series wiring connects outlets sequentially, with the output of one outlet feeding into the input of the next. This streamlined approach reduces the number of wire connections and simplifies the overall wiring process.
The straightforward nature of series wiring makes it particularly suitable for DIY enthusiasts or homeowners with basic electrical knowledge. By following a clear and logical sequence of connections, as outlined in a series diagram, even novice electricians can successfully wire outlets in series.
Moreover, the simplicity of series wiring can contribute to time and cost savings during installation. With fewer connections to make, electricians can complete the wiring process more efficiently, reducing labor costs. Additionally, the use of less wire can result in material cost savings compared to parallel wiring.
In conclusion, the simplicity of series wiring, as highlighted in the statement “Series wiring is relatively simple and straightforward to implement,” is a key advantage of this wiring method. It simplifies the wiring process, making it accessible to a wider range of individuals and offering potential cost savings.
Cost-effectiveness
The cost-effectiveness of wiring electrical outlets in series, as highlighted in the statement “It requires less wire and fewer connections compared to parallel wiring,” is a significant advantage of this wiring method. By reducing the amount of wire and the number of connections required, series wiring offers cost savings in both materials and labor.
- Reduced Material Costs: Series wiring requires less wire compared to parallel wiring. This is because, in a series circuit, the same wire carries the current through all the outlets, eliminating the need for multiple wires running from the power source to each outlet. The cost savings on wire can be substantial, especially in large-scale wiring projects.
- Fewer Connections: Series wiring also involves fewer connections compared to parallel wiring. In a series circuit, outlets are connected sequentially, with the output of one outlet connected to the input of the next. This reduces the number of individual connections that need to be made, saving time and effort during installation.
- Simplified Installation: The reduced number of connections in series wiring simplifies the installation process. With fewer connections to manage, electricians can complete the wiring more efficiently, reducing labor costs. The straightforward nature of series wiring also makes it more accessible to DIY enthusiasts or homeowners with basic electrical knowledge.
In summary, the cost-effectiveness of series wiring, achieved through reduced wire usage and fewer connections, contributes to overall project savings and makes it a practical choice for various electrical installations.
Flexibility
The flexibility offered by series wiring, as highlighted in the statement “Series wiring allows for greater flexibility in controlling multiple outlets from a single switch,” is a key advantage of this wiring method. By connecting outlets in series, electricians and homeowners gain greater control over the electrical system, allowing them to conveniently turn on or off multiple outlets simultaneously.
The use of a single switch to control multiple outlets is particularly useful in various scenarios. For instance, in a living room, a single switch can be used to control all the outlets powering lamps and other electrical devices, allowing for easy and centralized control of the room’s lighting. Similarly, in a bedroom, a series-wired outlet configuration can enable the control of multiple bedside outlets from a single switch, providing convenient access to power for devices like lamps, alarm clocks, and charging stations.
Furthermore, series wiring can be beneficial in outdoor applications. By connecting outdoor outlets in series and controlling them with a single switch, homeowners can easily turn on or off multiple outlets used for landscape lighting, water features, or other electrical equipment. This centralized control enhances convenience and safety, allowing for quick and effortless operation of outdoor electrical devices.
In summary, the flexibility offered by series wiring, as a component of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram,” provides greater control over electrical systems, enabling convenient and centralized operation of multiple outlets from a single switch. This flexibility is particularly advantageous in residential, commercial, and outdoor applications, offering practical solutions for managing electrical devices and enhancing overall efficiency.
Voltage Drop
In the context of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram,” understanding voltage drop is crucial. Voltage drop refers to the reduction in voltage that occurs as electricity flows through a circuit. This phenomenon is particularly relevant in series wiring, where the same current flows through each outlet in sequence.
When additional outlets are added to a series circuit, the total resistance of the circuit increases. As a result, the voltage drop across each outlet increases, leading to a decrease in the voltage available to each outlet. This voltage drop can become significant, especially in long circuits or when high-power devices are connected.
The practical significance of understanding voltage drop is to ensure that electrical devices receive adequate voltage to operate correctly. If the voltage drop is excessive, devices may not function properly or may even be damaged. Therefore, it is essential to consider the voltage drop when designing and installing series-wired circuits.
To mitigate voltage drop in series circuits, electricians can use larger gauge wires, which have lower resistance and reduce voltage drop. Additionally, they can limit the number of outlets connected in series and avoid connecting high-power devices to series circuits.
In summary, understanding voltage drop is a critical aspect of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram.” It helps electricians design and install circuits that provide adequate voltage to electrical devices, ensuring their proper operation and preventing potential damage.
Circuit Disruption
Understanding circuit disruption is a crucial aspect of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram.” Circuit disruption refers to the interruption of the flow of electricity in a circuit, which can occur due to a variety of factors, including a faulty outlet.
In a series circuit, all outlets are connected in sequence, meaning that the current flows through each outlet one after the other. If one outlet in the series fails, it creates an open circuit, preventing the current from flowing through the entire circuit. This open circuit disrupts the flow of electricity, causing all subsequent outlets in the series to lose power.
The practical significance of understanding circuit disruption is to ensure the reliable operation of electrical devices connected to the circuit. A faulty outlet can lead to unexpected power outages, affecting the functionality of appliances, lighting, and other electrical systems.
To prevent circuit disruption, it is essential for electricians to use high-quality outlets and to properly maintain the electrical system. Regular inspections and testing of outlets can help identify potential problems and prevent failures.
In summary, understanding circuit disruption is a critical component of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram.” It highlights the importance of using reliable components and maintaining the electrical system to ensure the uninterrupted flow of electricity and the proper operation of electrical devices.
Power Limitations
In the context of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram,” understanding power limitations is crucial for ensuring the safe and efficient operation of electrical circuits. Series wiring, while simple and cost-effective, may not be suitable for circuits that power high-wattage devices due to inherent limitations.
- Current Capacity: Series wiring involves connecting outlets sequentially, with the same current flowing through each outlet. High-power devices, such as major appliances or power tools, draw significant current. If the current demand exceeds the capacity of the circuit, it can lead to overheating, damage to components, and potential fire hazards.
- Voltage Drop: As current flows through a series circuit, there is a gradual decrease in voltage across each outlet. This voltage drop becomes more pronounced with longer circuits or when multiple high-power devices are connected. Excessive voltage drop can result in insufficient voltage reaching the devices, causing them to malfunction or operate below optimal levels.
- Circuit Protection: Electrical circuits are typically protected by fuses or circuit breakers, which trip when the current exceeds a safe limit. In a series circuit, a fault in one outlet can cause the entire circuit to trip, interrupting power to all subsequent outlets. This can be inconvenient and potentially hazardous, especially if critical devices are connected.
- Code Compliance: Electrical codes and standards often specify the maximum number of outlets and the types of devices that can be connected to a series circuit. Exceeding these limits can void warranties, increase the risk of electrical problems, and compromise safety.
Therefore, when designing and installing electrical circuits, it is essential to consider the power requirements of the devices that will be connected. If high-power devices are involved, parallel wiring or dedicated circuits should be used to ensure adequate power and prevent potential hazards associated with series wiring.
Creating “Wiring Electrical Outlets in Series Diagram”
Wiring electrical outlets in series involves connecting outlets sequentially, with the output of one outlet serving as the input for the next. This method of wiring differs from parallel wiring, where each outlet receives power directly from the electrical panel. A series diagram illustrates the sequence of connections, showing the flow of electricity from the power source through each outlet.
Creating a “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram” can be helpful for visualizing the layout of the circuit and ensuring that it is wired correctly. Here are the steps to create a series diagram:
- Draw the power source: Start by drawing the power source, which is typically represented by a rectangle or circle. Label the power source with the appropriate voltage and amperage.
- Draw the first outlet: Draw the first outlet in the series, which is connected to the power source. Label the outlet with the appropriate amperage and voltage.
- Connect the outlets: Continue drawing the outlets in the series, connecting each outlet to the previous one. Label each outlet with the appropriate amperage and voltage.
- Draw the load: Finally, draw the load, which is the device or appliance that will be powered by the circuit. Label the load with the appropriate amperage and voltage.
Here are some examples of “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram”:
- Simple series circuit: A simple series circuit consists of a power source, a single outlet, and a load. This type of circuit is commonly used for small appliances, such as lamps or fans.
- Series circuit with multiple outlets: A series circuit with multiple outlets consists of a power source, multiple outlets, and a load. This type of circuit is commonly used for powering multiple devices in a room, such as a computer, printer, and monitor.
- Series circuit with a switch: A series circuit with a switch consists of a power source, a switch, multiple outlets, and a load. This type of circuit allows you to control the power to multiple outlets with a single switch.
Creating a “wiring electrical outlets in series diagram” is a useful way to visualize the layout of a circuit and ensure that it is wired correctly. By following the steps outlined above, you can create a clear and concise diagram that will help you to troubleshoot and maintain your electrical system.
Frequently Asked Questions about Wiring Electrical Outlets in Series
Wiring electrical outlets in series is a common and cost-effective method for powering multiple outlets from a single circuit. However, there are some important considerations to keep in mind when wiring outlets in series. Here are answers to some frequently asked questions about this topic:
Question 1: What are the advantages of wiring electrical outlets in series?
Wiring outlets in series offers several advantages. It is relatively simple and cost-effective, requiring less wire and fewer connections compared to parallel wiring. Additionally, series wiring provides greater flexibility in controlling multiple outlets from a single switch.
Question 2: What are the disadvantages of wiring electrical outlets in series?
The main disadvantage of wiring outlets in series is that the current flowing through each outlet is the same. This means that adding additional outlets to the circuit will decrease the voltage available to each outlet. Additionally, if one outlet in the series fails, it can disrupt the entire circuit.
Question 3: When is it appropriate to use series wiring?
Series wiring is suitable for low-power applications, such as powering lights or small appliances. It is also a good option for situations where you want to control multiple outlets from a single switch.
Question 4: When should you avoid using series wiring?
Series wiring should be avoided for high-power applications, such as powering major appliances or power tools. Additionally, series wiring should not be used in circuits that require a consistent voltage supply, as the voltage drop can cause problems for sensitive electronic devices.
Question 5: How do you calculate the voltage drop in a series circuit?
The voltage drop in a series circuit can be calculated using Ohm’s law: V = IR, where V is the voltage drop, I is the current, and R is the resistance. The resistance of each outlet can be found by consulting the manufacturer’s specifications.
Question 6: Can I mix series and parallel wiring in the same circuit?
Yes, it is possible to mix series and parallel wiring in the same circuit. However, it is important to carefully plan the circuit to ensure that the voltage and current requirements of all the devices are met.
These are just a few of the frequently asked questions about wiring electrical outlets in series. For more information, consult a qualified electrician.
Wiring electrical outlets in series can be a safe and effective way to power multiple outlets from a single circuit. By understanding the advantages and disadvantages of series wiring, you can make informed decisions about when to use this method.
Conclusion
Wiring electrical outlets in series is a simple and cost-effective method for powering multiple outlets from a single circuit. However, it is important to understand the advantages and disadvantages of series wiring before using it in your home or business.
Series wiring is best suited for low-power applications, such as powering lights or small appliances. It is also a good option for situations where you want to control multiple outlets from a single switch. However, series wiring should be avoided for high-power applications, such as powering major appliances or power tools. Additionally, series wiring should not be used in circuits that require a consistent voltage supply, as the voltage drop can cause problems for sensitive electronic devices.
If you are considering wiring electrical outlets in series, it is important to consult with a qualified electrician to ensure that the circuit is designed and installed safely and correctly.
By understanding the basics of wiring electrical outlets in series, you can make informed decisions about when to use this method and how to ensure that your electrical system is safe and efficient.
Youtube Video: